Strep throat is a common bacterial infection that is caused by a bacterium known as Group A Streptococcus or (GAS). Although strep throat is an infection that can easily be treated with simple antibiotics, if left untreated, it can lead to dangerous complications such as rheumatic heart fever. These complications are especially prevalent in developing countries. However, residents of developed countries are not immune to these strep throat complications.
A precise diagnosis of strep throat can be challenging; individuals who carry strep bacteria in their throats, but have no symptoms at all, are known as carriers. Although these strep throat carriers are asymptomatic, they are still contagious and can transmit the virus, especially in crowded places like dorms and camps (sound familiar?).
Strep Throat Antibiotics
Recommendations on treating strep throat carriers with antibiotics vary widely between countries. For example, in France, Finland, and the United States, treating everyone who tested positive for strep throat is the recommended course of action regardless of being symptomatic or not. In this case, strep throat antibiotics will be prescribed. On the other hand, in New Zealand, a strep throat-positive patient should be symptomatic first to receive treatment for strep throat. For physicians and policymakers, it's really a matter of weighing the risks and benefits of antibiotic therapy to hang in balance between preventing strep throat serious complications and minimizing inappropriate antibiotic prescriptions.
Reports on the rates of strep throat infection and carriage vary considerably from one setting to another and between age groups. For example, the prevalence of strep throat carriage was approximately 10% of school-aged children. And this figure drops to 7% strep throat carriage when considering the general population.
The Importance of Testing Prior to Strep Throat Antibiotics
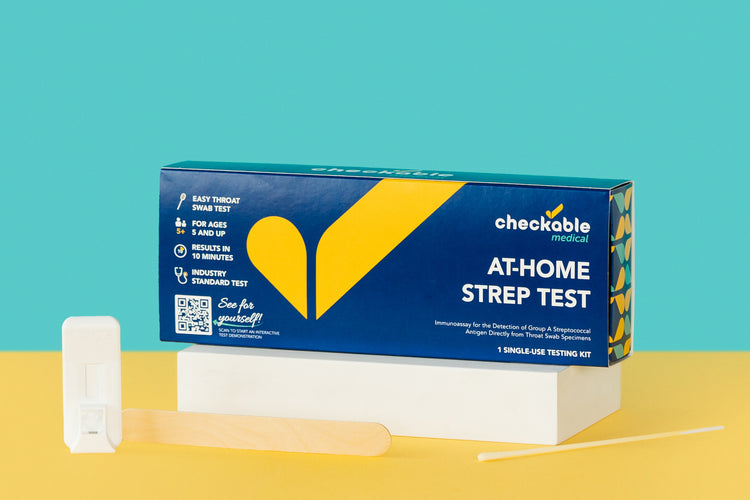
Due to the damaging effects of inappropriate antibiotic use on the environment and human health, it is crucial to target strep throat management and testing in the most efficient and effective way. Recent development in testing capabilities has led to the creation of rapid testing methods that can detect strep throat infection in a matter of minutes. There are two methods of testing that are widely used for strep throat infection: throat bacterial cultures and rapid antigen detection methods. Testing for strep is the only way to know if strep bacteria are present. You can now do the rapid strep tests at home or your doctor's.
A study was performed to detect asymptomatic strep throat carriage across different countries and age groups. The 5-19 years old age group had the highest rate of strep throat carriage since nearly a quarter of them were found to be strep throat carriers. The rate of strep throat complications is greater in developing countries compared to higher-income countries. However, when studying the rate of strep throat carriage among populations, the researchers found that the percentage of strep throat carriers is slightly higher among income countries when compared to lower-income countries (6% in lower-income countries, compared to 7% in higher-income countries). This can be due to the low strep throat detection capabilities in lower-income countries compared to higher-income countries.
Strep throat carriers can be an issue in the efforts to prevent strep throat infection. Detecting them using all testing capacities is important for the treatment of strep throat, but also in the proper strep throat antibiotics prescription.
Life is too short to sit in a doctor’s office
Sign up for our weekly newsletter and get valuable healthcare tips and tricks in your inbox!
Sign up now and unsubscribe anytime.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Press the space key then arrow keys to make a selection.