Understanding the Physical and Emotional Changes During the Second Half of an Antibiotic Treatment
Checkable Health
Antibiotics are a group of medications used to treat certain infections caused by bacteria. Many kinds of antibiotics treat various conditions, such as pneumonia and other respiratory infections, strep throat (streptococcus infection), urinary tract infections, and skin infections, to name a few. They work by stopping the growth of bacteria. After you start taking a course of antibiotics, you will likely have some symptom relief. This blog post will explain how you can expect to feel in the second half of your antibiotics course.
What Side Effects Can I Expect During the Second Half of the Antibiotic Treatment Cycle?
You might notice a difference in how you feel in the second half of your antibiotic treatment cycle. The side effects can depend on how you take the medication, which medication it is, and how strong the dose is. Most antibiotics are taken orally, or by mouth, but there are many ways to administer antibiotics, such as topically, in eye drops, or as an injection. Below are some of the most common side effects of most oral antibiotics:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and upset stomach
- Candida or yeast infection
A less talked about side effect of antibiotics is depression and anxiety, which can happen during or after completing the cycle. The bacterial flora or "microbiome" in our intestines is responsible for a lot of our mood and feelings of well-being. Surprisingly, many of the hormones and neurotransmitters the brain uses to communicate our feelings are made in the gut. The gut can only make the right chemicals for our brain if the correct bacteria are there to give it what it needs. Taking antibiotics decreases the total bacterial load of the body, even the beneficial ones that help this process. When the bacterial numbers are off balance, that can affect how we feel. Because of this, taking care of our mental health is essential while on and after taking antibiotics.
Additionally, some people can have an allergic reaction to the antibiotics they are taking. If you notice any of these symptoms, stop taking the medication and seek medical attention immediately.
- Itching
- Rash
- Hives
- Swelling of the face, tongue, or lips
- Wheezing
- Difficulty breathing
How Long Will It Take for the Antibiotic to Clear My System Completely?
Each antibiotic is different in how long it takes to leave the body. Common antibiotics may stay in your system for 24 hours after the last dose. Higher doses or other medications may take longer to clear the body. The adverse effects from antibiotics, such as gut balance issues, yeast infection, anxiety, and depression, may last long after you stop taking the medication.
How Can I Tell If My Symptoms Are Improving During the Second Half of the Treatment?
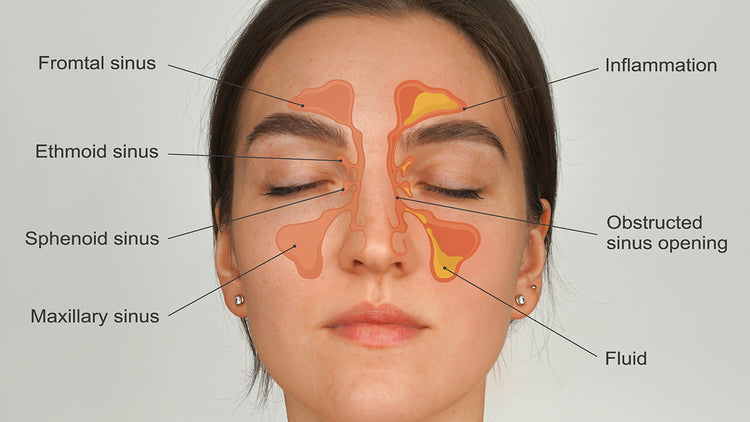
You will know your symptoms are improving if you start to feel better. For instance, if you take antibiotics for a sinus infection, you might notice less pressure in your nose; breathing out of your nose becomes easier, and your overall energy increases. If you feel like your symptoms are improving in the second half of your antibiotic course, it might be time to discuss with your doctor about stopping the medication.
The Finishing Antibiotics Myth
The long-standing advice is that you need to finish your full antibiotics course. However, recent studies show that it might be ok to stop when you are no longer symptomatic. The study from the Medical Journal of Australia noted that stopping a course of antibiotics once the symptoms have subsided is a reasonable action, and it is not likely to lead to antibiotic resistance or a relapse of symptoms. This result is good news if your body is having side effects or reactions to the antibiotic. You could stop them when you feel like your symptoms have resolved and not have to continue to have side effects from taking the medication.
Taking an antibiotic when it isn't needed increases the chance of it not working for you in the future. If you needed to take that antibiotic, there would be a chance of the bacteria not being susceptible to that particular medication. This reason is why healthcare providers should only prescribe antibiotics if they are absolutely necessary.
Stopping the antibiotic when the infection symptoms are gone is reserved for mild and moderate cases. In the case of severe illness or infection, the entire course of treatment and higher doses of the medication might be more appropriate.
Lifestyle Changes to Enhance the Effectiveness of the Antibiotic
There are things you can do as a patient to enhance the effectiveness of the antibiotic and help ward off any unwanted side effects.
Probiotics
An antibiotic’s job is to rid the body of harmful bacteria, but sometimes they take beneficial bacteria with them. It can be helpful to take probiotics while on a course of antibiotics. Some evidence shows probiotics can enhance and restore normal intestinal flora. Probiotics can also help with diarrhea if you happen to develop that condition.
Diet and Lifestyle
You will likely be able to resume your regular diet while on antibiotics, but you'll want to make healthier choices to increase your chance of healing faster. Avoid highly processed food, smoking of any kind, and alcohol if you want your body to repair and get rid of the offending pathogen. Stick with foods from nature and lots of clean water. Add probiotic foods like yogurt, kefir, and other fermented foods for a bonus.
Mental Health
Since you are more likely to feel anxious or depressed when taking an antibiotic, taking care of your mental health needs to be at the top of your list. Rest, laugh, and enjoy friends and family as much as possible. Speak to your doctor or a mental health professional about how you are feeling.
Is It Normal to Experience Worsening Symptoms During the Second Half of the Antibiotic Treatment Cycle?
Since antibiotics can have adverse side effects, it is good to know what to look for in the second half of the course of your treatment. Depending on the severity of your condition, you could have a recurrence of symptoms. If you feel worse, you'll want to return to your doctor and get evaluated to ensure you are on the correct medication. You could feel worse if you are taking an antibiotic that you don't need.
Antibiotics are sometimes necessary and life-saving, but they aren’t without risk. The side effects can have you feeling as bad as the infection you're taking them for. Check with your provider to ensure that you are on the medication you need and that you don't have to be on it when you don't need it. This step will reduce the adverse side effects and antibiotic resistance that can occur.
References
Bpac. (2015). Is it ok to stop antibiotics when symptoms resolve?. Best Practice Journal, 68. https://bpac.org.nz/bpj/2015/june/symptoms.aspx
Dinan, K., & Dinan, T. (2022, July 12). Antibiotics and mental health: The good, the bad and the ugly. Journal of Internal Medicine, 292(6), 858-869. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/joim.13543#:~:text=Overall%2C%20antibiotics%20increase%20the%20prevalence,to%20keep%20this%20in%20mind.
Medline Plus. (2022, January 15). Amoxicillin. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a685001.html
Pope, C. (2022, November 7). Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?. Drugs.com. https://www.drugs.com/medical-answers/probiotics-with-antibiotics-3121702/

Hayley Ferut RN, BSN, IBCLC
My name is Hayley Ferut, and I have 10 years of combined experience as a Registered Nurse and International Board Certified Lactation Consultant. My professional passions include birth, breastfeeding, mental health, and patient education. I strive to deliver high quality health care content while being a mom to my precious little boys. I write to educate patients and clients so they can make informed decisions about their health.
Life is too short to sit in a doctor’s office
Sign up for our weekly newsletter and get valuable healthcare tips and tricks in your inbox!
Sign up now and unsubscribe anytime.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Press the space key then arrow keys to make a selection.